Solid state drives (SSDs) and hard disk drives (HDDs) can store and arrange data using two alternative disk partitioning schemes: GPT (GUID Partition Table) and MBR (Master Boot Record). Today, we’ll examine their benefits and drawbacks and advise you on HDD and SSD selection. MBR or GPT – which is better to choose for the disk?
What is MBR
Hard drives and other storage devices require the MBR (Master Boot Record), which is essential to the way a computer boots up. It is a tiny but crucial partition that starts at the very beginning of the disk and holds the data required for the operating system to launch successfully.
Components of MBR:
- Bootloader: This is a mini-program that is responsible for loading the operating system. It determines which operating system is installed on the disk and loads it into the computer’s memory;
- Partition table: This table contains information about the four main partitions of the disk. Each partition can contain a separate operating system, file system, or data;
- Magic signature: This is a unique verification code that is used to verify the integrity of the MBR. If the magic signature is damaged, the computer will not be able to boot.
MBR has been the standard for disk partitioning for many years and is still used on:
- Older computers: MBR is compatible with older BIOSs and operating systems such as Windows XP and earlier;
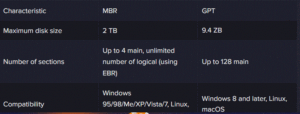
- Small drives: MBR is suitable for drives up to 2 terabytes (TB).
Pros and cons of MBR
Pros of MBR
- Widely Compatible: MBR is supported by almost all operating systems, including Windows, Linux and macOS. This makes it a versatile choice for users working on different platforms;
- Simplicity: The MBR structure is quite simple and straightforward, which makes working with disk partitions easier. This advantage is especially important for novice users and computer service professionals;
- Easy recovery: Due to their simple structure, recovering data from MBR disks in the event of damage is usually not particularly difficult.
Cons of MBR
- Disk size limitation: MBR supports disks up to 2 TB. With the growing volumes of modern hard drives and SSD drives, this limitation is becoming increasingly critical;
- Limited number of partitions: MBR supports only four primary partitions. To create more partitions, you need to use extended partitions, which adds complexity to an already limited structure;
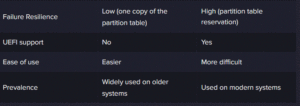
- No backup MBR: The MBR is stored in only one location on the disk. Damage to this area may result in loss of access to the entire contents of the disk.
Although it is no longer in use, MBR disk partitioning is still common. GPT is replacing MBR in many modern systems because it offers a more dependable and adaptable partition management framework while also addressing many of MBR’s shortcomings.
What is GPT
The contemporary disk partitioning system known as GPT (GUID Partition Table) was created to address the shortcomings of the outdated MBR (Master Boot Record). Due to its many benefits, GPT is progressively taking the place of MBR in the high-performance systems of today.
Rather than using 32-bit MBR entries to identify partitions, GPT employs 64-bit unique identifiers (GUIDs). This enables GPT to:
- Support drives up to 9.4 zettabytes (ZB), well beyond the 2 terabyte MBR limit;
- Create up to 128 primary partitions, compared to four primary and unlimited logical partitions in the MBR;
- Improve fault tolerance by reserving the partition table in multiple locations on the disk.
GPT is used by most new computers. They come with GPT and UEFI pre-installed. GPT is also recommended for SSDs and hard drives larger than 2 TB.
Pros and cons of GPT
Pros of GPT
- No disk space limitation: GPT is ideal for modern high-capacity SSD drives;
- More partitions: GPT provides flexibility in data organization, allowing you to create more partitions without using complex extended partition schemes;
- Improved Reliability: Partition table backup reduces the risk of data loss due to MBR corruption;
- UEFI Compatible: GPT is the standard disk partitioning scheme for UEFI systems, replacing BIOS.
Cons of GPT
- Incompatibility with older systems: GPT does not work with older BIOS systems and some operating systems such as Windows XP and earlier;
- Requirement of UEFI: GPT requires UEFI to boot from a GPT disk.
Comparison of MBR and GPT
What to choose – MBR or GPT
a succinct response to the query, “Is MBR or GPT better?” No, because it all depends on what you need specifically. GPT is typically a more up-to-date and trustworthy option, with the following exceptions:
- Using an old computer with BIOS and Windows XP or earlier;
- Prefer the simplicity of MBR.
Use GPT on new computers as it is pre-installed on the majority of contemporary UEFI and SSD devices. If compatibility with older systems is needed, use MBR on the older ones.
Since MBR is the default partitioning strategy for UEFI and does not support devices larger than 2TB, utilize GPT for larger drives. MBR or GPT – which is better to choose for the disk?
Also Read: How to partition a hard drive in Windows 10
Also Read: How to set up startup in Windows 10